“Wildfire digital twin” of the Earth: OroraTech grabs €37M to scale satellite-powered fire intelligence
Wildfires are a rapidly escalating global problem, intensified by climate change that brings more frequent and severe droughts and fire-favourable weather patterns. These conditions make landscapes increasingly susceptible to devastating, fast-spreading fires. The consequences are dire: wildfires destroy 30–40 million hectares of vegetation annually, cause over $20 billion in insured losses, emit billions of tons of CO₂, and threaten biodiversity, infrastructure, and human lives. OroraTech addresses these challenges with an integrated, end-to-end wildfire management platform powered by proprietary thermal infrared satellites, advanced AI analytics, and seamless data delivery.
OroraTech has extended its Series B funding round to €37 million, led byBNP Paribas Solar Impulse Venture Fundand Rabo Ventures, with continued support from existing investors Bayern Kapital, Edaphon, and the European Circular Bioeconomy Fund (ECBF). This extension brings significant backing from two of Europe’s leading banks. It follows the company’s rapid commercial growth, having secured nearly €100 million in contracts and venture capital over the past year.
The funding will accelerate OroraTech’s expansion as a global provider of wildfire intelligence and thermal data infrastructure. With ten proprietary thermal-sensing satellites already in orbit, OroraTech delivers persistent, real-time wildfire detection and risk assessment, enabling the creation of a “wildfire digital twin” of the Earth. This platform allows users, including governments and industries, to monitor, simulate, and predict wildfire behaviour worldwide, 24/7, with unprecedented accuracy.
OroraTech was founded in 2018 in Munich, Germany, as a spin-off from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) byThomas Grübler,Björn Stoffers,Rupert Amann, andFlorian Mauracher. The founders gained hands-on experience building and operating small satellites through involvement in TUM’s student satellite research groups, particularly the MOVE-II CubeSat project and WARR.
They launched OroraTech to address the urgent need for better global wildfire detection and climate monitoring. Their motivation came from identifying significant gaps in existing Earth observation data, especially thermal-infrared imagery, and recognising the growing threat of wildfires due to climate change. By leveraging their satellite technology expertise, they aimed to create a satellite-based early warning system for continuous, real-time monitoring of wildfires and other climate-related phenomena to protect people, property, and the environment.
Strategic partnerships have further propelled OroraTech’s growth. Collaborations with Isar Aerospace enable flexible launches for its nanosatellite constellation. At the same time, a collaboration with Spire Global facilitated the deployment of its first thermal-infrared payload using Spire’s satellite network for rapid data transmission. In 2025, OroraTech joined the GREEN+ Programme to monitor millions of hectares of protected forests globally, supporting biodiversity and carbon stock preservation in South America and beyond.
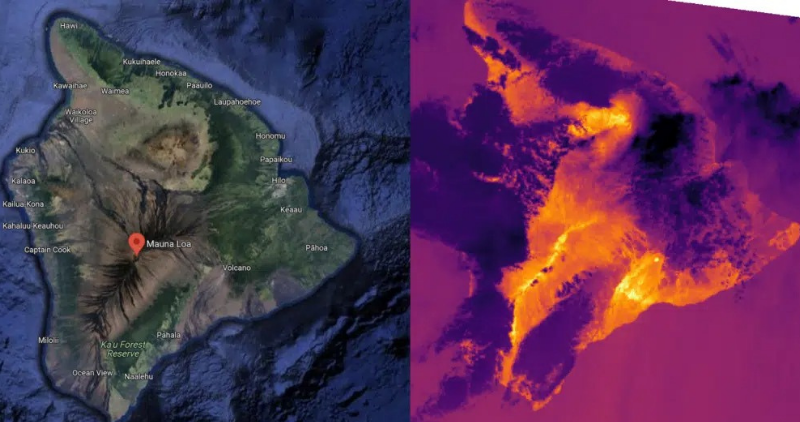
OroraTech distinguishes itself in the wildfire detection market through its proprietary constellation of thermal infrared satellites, designed explicitly for real-time fire monitoring. Unlike traditional satellites that rely mainly on optical sensors and often provide delayed or incomplete data, OroraTech’s satellites can detect temperature anomalies day and night, through smoke and clouds, and even in remote or inaccessible regions.
In the competitive landscape, OroraTech faces rivals like Planet Labs, Fireball International, Descartes Labs, BlackSky, and IQ FireWatch. While these companies offer valuable Earth observation or wildfire detection services, they often rely on optical data, have slower detection times, or are limited to specific regions or ground-based infrastructure. OroraTech’s dedicated, scalable satellite constellation and rapid, software-driven alert system set it apart, enabling faster, more reliable wildfire intelligence and giving stakeholders crucial time to protect people, property, and the environment.
The company’s satellites feature advanced onboard AI and edge computing capabilities, processing and analysing data directly in space. This allows OroraTech to deliver actionable wildfire alerts to users within minutes of detection — a dramatic improvement over conventional systems’ hours-long delays.
OroraTech’s Forest satellite series demonstrates this technical advancement. Forest-1, launched in 2022, featured passive cooling and onboard GPU processing to reduce detection latency. Forest-3, launched in 2025, introduced AI-driven, real-time alerts via a three-channel thermal infrared system and X-band downlinks, achieving 4×4-meter spatial resolution.
The satellites’ mid-wave infrared (MWIR) sensors detect active fires, while long-wave infrared (LWIR) sensors identify smouldering zones through smoke. Onboard edge computing compresses data in orbit, enabling alerts within 3 minutes via inter-satellite links, starkly contrasting traditional systems’ hour-long delays.
Another key differentiator is OroraTech’s high spatial resolution. Their sensors can identify hotspots as small as 4×4 meters, enabling early detection of small fires before they escalate into major disasters. The solution is delivered as a cloud-based software platform and API, requiring no additional hardware for end users.
Beyond early detection, OroraTech offers specialised tools like Fire Spread, which predicts fire movement using wind, vegetation, and elevation data. This feature enabled Chilean forestry company ARAUCO to allocate resources effectively during the 2024 El Quillay fire, reducing containment times.
The Burnt Area Mapping tool, with 10-meter resolution, aids insurers and agricultural firms in post-fire recovery by quantifying biomass loss and validating claims. The Land Surface Temperature (LST) product, recognised by the IPCC as an Essential Climate Variable, supports urban heat island mitigation and precision agriculture. These innovations establish OroraTech as a holistic wildfire management platform rather than a mere detection service.
OroraTech’s customer base and impact are substantial. Suzano, a Brazilian cellulose giant, uses OroraTech to monitor 2.7 million hectares, complementing ground cameras with orbital oversight during night and remote-area fires. The European Union integrates OroraTech’s data into its Copernicus program for emergency response and climate analysis. In 2022, OroraTech protected 183 million hectares of forests, reducing CO₂ emissions by 41% and potentially saving lives from wildfire-related air pollution.
OroraTech’s 2025 collaboration with NVIDIA Earth-2 embeds its thermal data into a climate digital twin, enhancing extreme weather predictions. This builds on prior use of NVIDIA Jetson modules for onboard AI processing. The company also uses Google Cloud for scalable data infrastructure, training machine learning models with Vertex AI to improve detection accuracy.
Looking ahead, OroraTech plans to deploy a constellation of 100+ satellites by 2026 to achieve 30-minute global revisit times. Upcoming features include mobile-optimised Fire Spread simulations for field commanders and automated updates via expanding thermal sensor networks. These efforts aim to solidify Ororatech’s position as the “thermal intelligence backbone” for climate resilience.

Published on Other News Site












